Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Reduce model size by using the mesh skin for result and mesh extraction#
This example shows postprocessing on a mesh skin for a static analysis. The skin mesh is rebuilt with new surface elements connecting the nodes on the external skin of the solid mesh. These surface elements types are chosen with respect to the solid elements facets having all their nodes on the skin.
This feature, available for all types of mechanical simulation, allows you to reduce the size of both the mesh and the extracted data to improve processing performance. Because larger stresses and strains are usually located on the skin of a model, computing results on the skin gives equivalent maximum values in most cases.
Postprocessing of elemental or elemental nodal results requires element solid to skin mapping to get from a solid element result to a facet result. Because the connectivity of the new surface elements built on the skin are different from the connectivity of the solid elements, small differences can be found after result averaging.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports. This example uses a supplied file that you can
get using the examples module.
from ansys.dpf import post
from ansys.dpf.post import examples
Get Simulation object#
Get the Simulation object that allows access to the result. The Simulation
object must be instantiated with the path for the result file. For example,
"C:/Users/user/my_result.rst" on Windows or "/home/user/my_result.rst"
on Linux.
example_path = examples.download_crankshaft()
# to automatically detect the simulation type, use:
simulation = post.load_simulation(example_path)
# to enable auto-completion, use the equivalent:
simulation = post.StaticMechanicalSimulation(example_path)
# print the simulation to get an overview of what's available
print(simulation)
Static Mechanical Simulation.
Data Sources
------------------------------
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.10.19/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ansys/dpf/core/examples/result_files/crankshaft/crankshaft.rst
DPF Model
------------------------------
Static analysis
Unit system: MKS: m, kg, N, s, V, A, degC
Physics Type: Mechanical
Available results:
- node_orientations: Nodal Node Euler Angles
- displacement: Nodal Displacement
- velocity: Nodal Velocity
- acceleration: Nodal Acceleration
- reaction_force: Nodal Force
- stress: ElementalNodal Stress
- elemental_volume: Elemental Volume
- stiffness_matrix_energy: Elemental Energy-stiffness matrix
- artificial_hourglass_energy: Elemental Hourglass Energy
- kinetic_energy: Elemental Kinetic Energy
- co_energy: Elemental co-energy
- incremental_energy: Elemental incremental energy
- thermal_dissipation_energy: Elemental thermal dissipation energy
- elastic_strain: ElementalNodal Strain
- elastic_strain_eqv: ElementalNodal Strain eqv
- element_orientations: ElementalNodal Element Euler Angles
- structural_temperature: ElementalNodal Structural temperature
------------------------------
DPF Meshed Region:
69762 nodes
39315 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
------------------------------
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 3
Cumulative Time (s) LoadStep Substep
1 1.000000 1 1
2 2.000000 1 2
3 3.000000 1 3
Extract displacement data#
Extract displacement data on the skin.
displacement_skin = simulation.displacement(skin=True)
displacement_skin.plot()
print(f"number of nodes with skin=True: {len(displacement_skin.index.mesh_index)}")
print(f"number of nodes with skin=False: {len(simulation.mesh.node_ids)}")
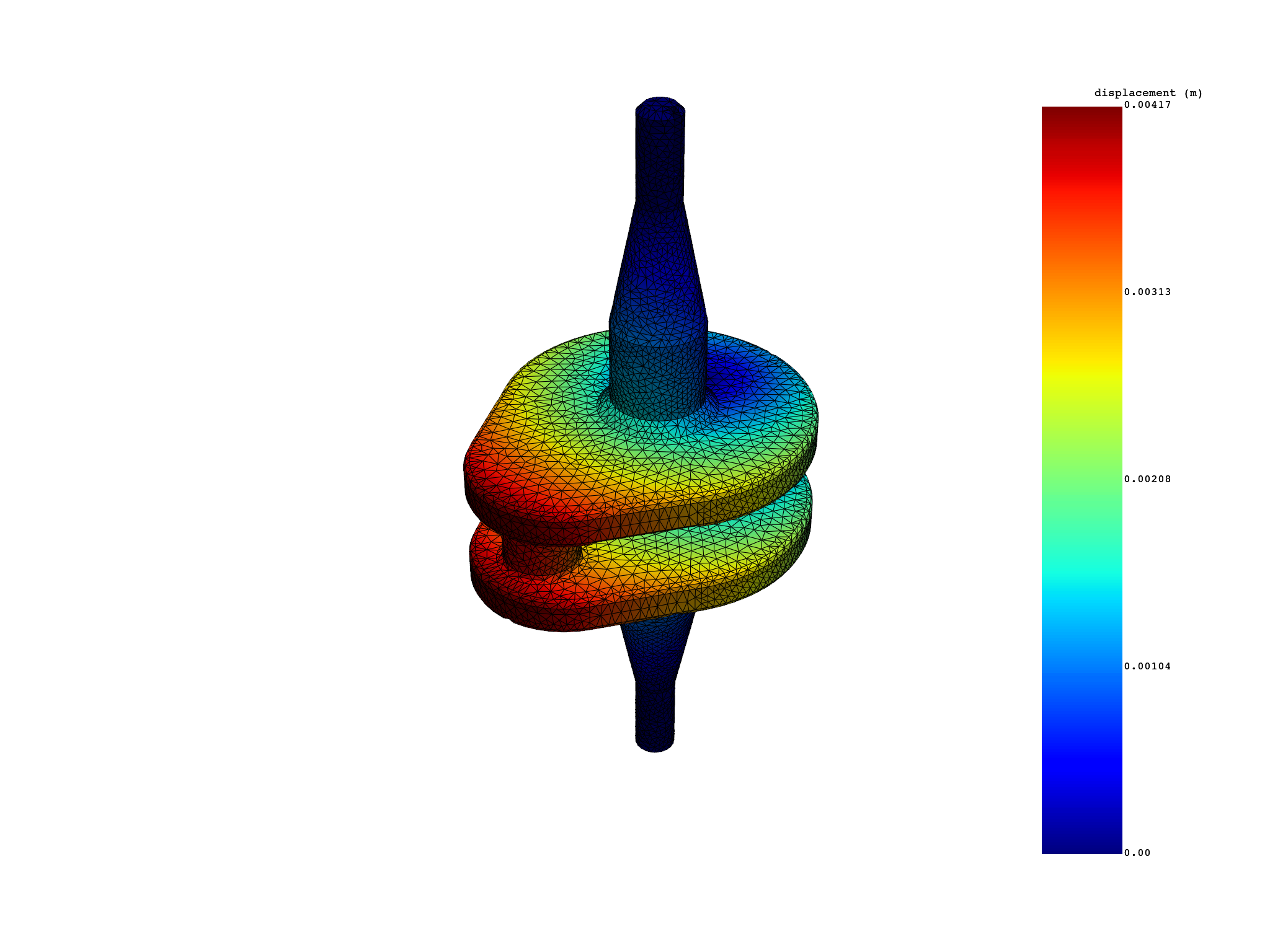
number of nodes with skin=True: 32922
number of nodes with skin=False: 69762
Extract stress and strain data#
Extract stress and elastic strain data on the skin. Compute averages and invariants through a solid-to-skin connectivity mapping.
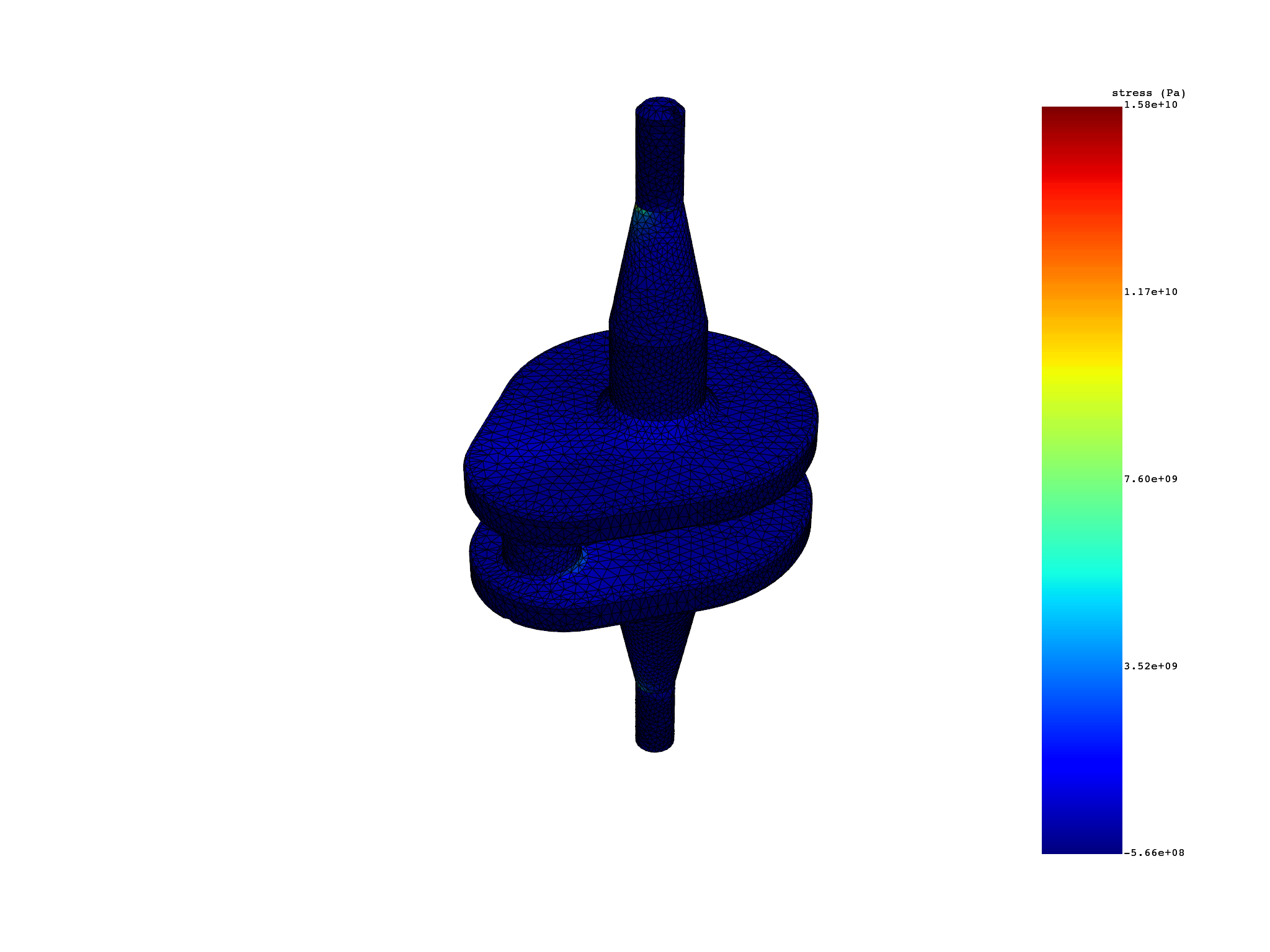
elemental_stress_skin = simulation.stress_principal_elemental(components=[1], skin=True)
elemental_stress_skin.plot()
print(
f"number of elements with skin=True: {len(elemental_stress_skin.index.mesh_index)}"
)
print(f"number of elements with skin=False: {len(simulation.mesh.element_ids)}")
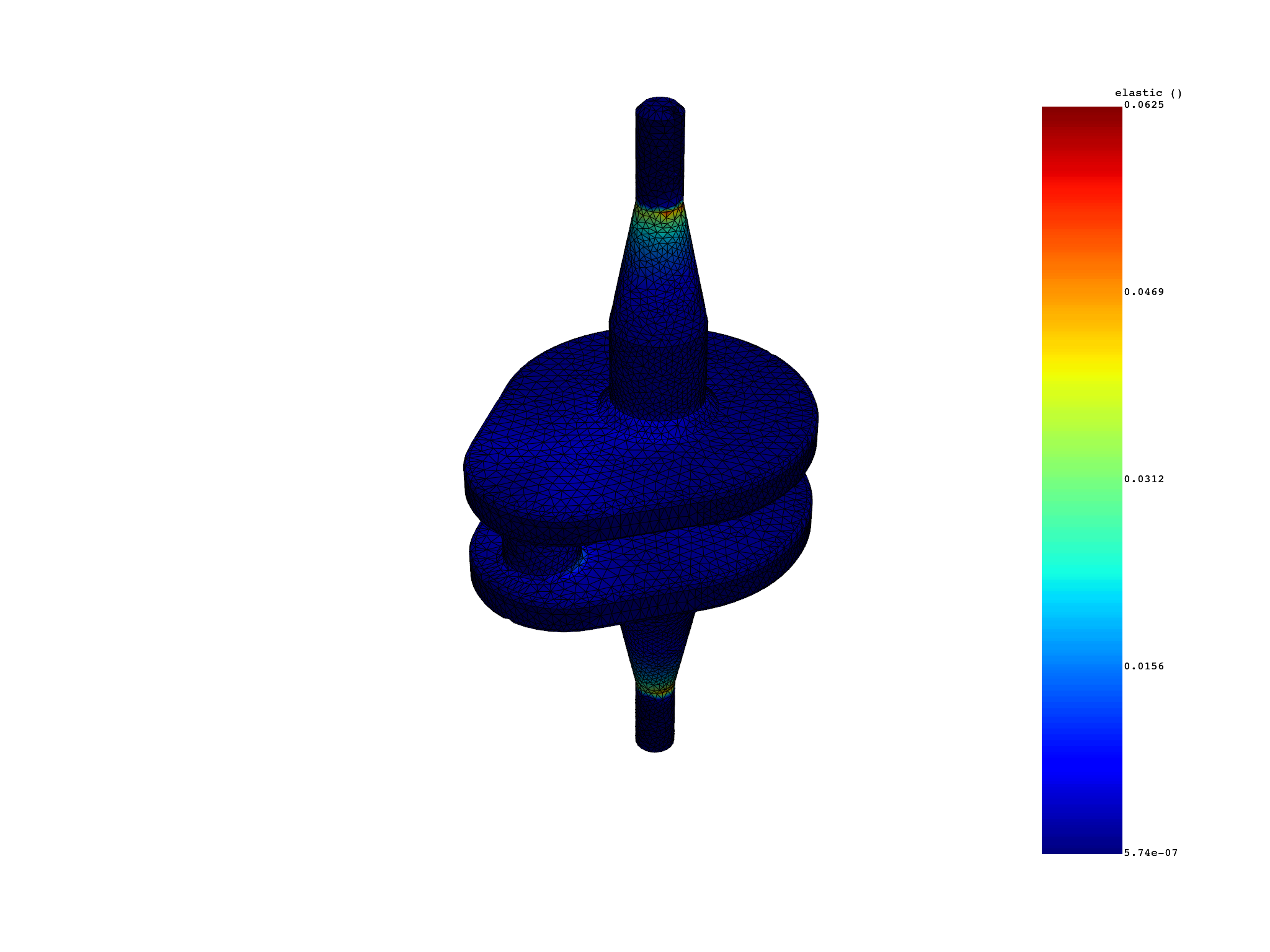
elastic_strain_eqv_skin = simulation.elastic_strain_eqv_von_mises_nodal(skin=True)
elastic_strain_eqv_skin.plot()
number of elements with skin=True: 16460
number of elements with skin=False: 39315
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f7716612bc0>)
Extract external layer on a selection of elements#
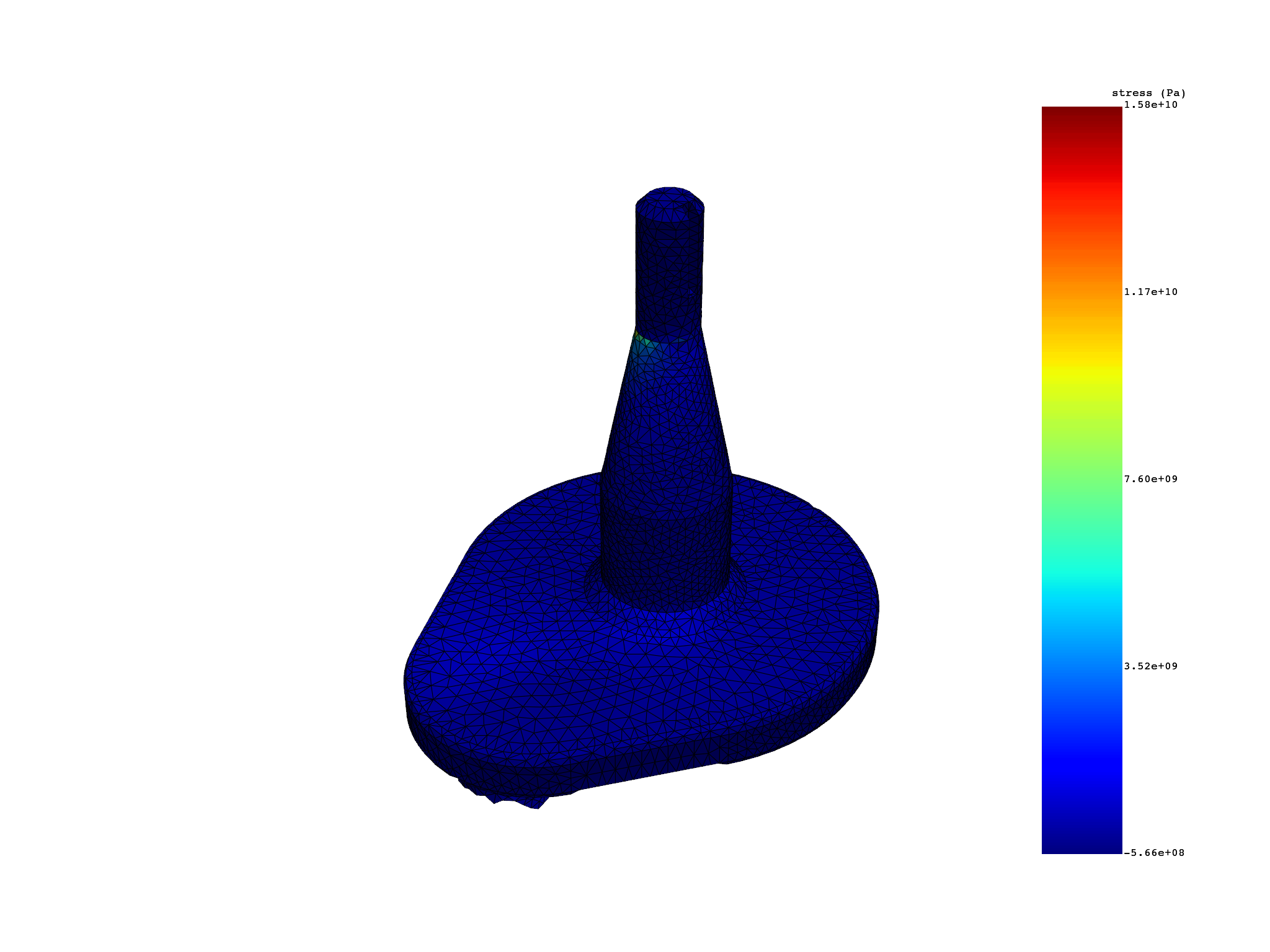
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f7716610c10>)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.114 seconds)