PyDPF-Post#
Ansys Data Processing Framework (DPF) provides numerical simulation users and engineers with a toolbox for accessing and transforming simulation data. With DPF, you can perform complex preprocessing or postprocessing of large amounts of simulation data within a simulation workflow.
The Python ansys-dpf-post package provides a high-level, physics-oriented API for postprocessing. Loading a simulation (defined by its results files) allows you to extract simulation metadata and results and then apply postprocessing operations on them.
The latest version of DPF supports Ansys solver results files for:
Mechanical APDL (.rst, .mode, .rfrq, .rdsp)
LS-DYNA (.d3plot, .binout)
Fluent (.cas/dat.h5, .flprj)
CFX (.cad/dat.cff, .flprj)
For more information on file support, see the main page in the PDF-Core documentation.
PyDPF-Post leverages the PyDPF-Core project’s ansys-dpf-core package, which is
available at PyDPF-Core GitHub.
Use the ansys-dpf-core package for building more advanced and customized
workflows using DPF.
Brief demo#
Provided you have Ansys 2023 R1 or later installed, a DPF server automatically starts once you start using PyDPF-Post.
To load a simulation for a MAPDL result file to extract and postprocess results, use this code:
>>> from ansys.dpf import post
>>> from ansys.dpf.post import examples
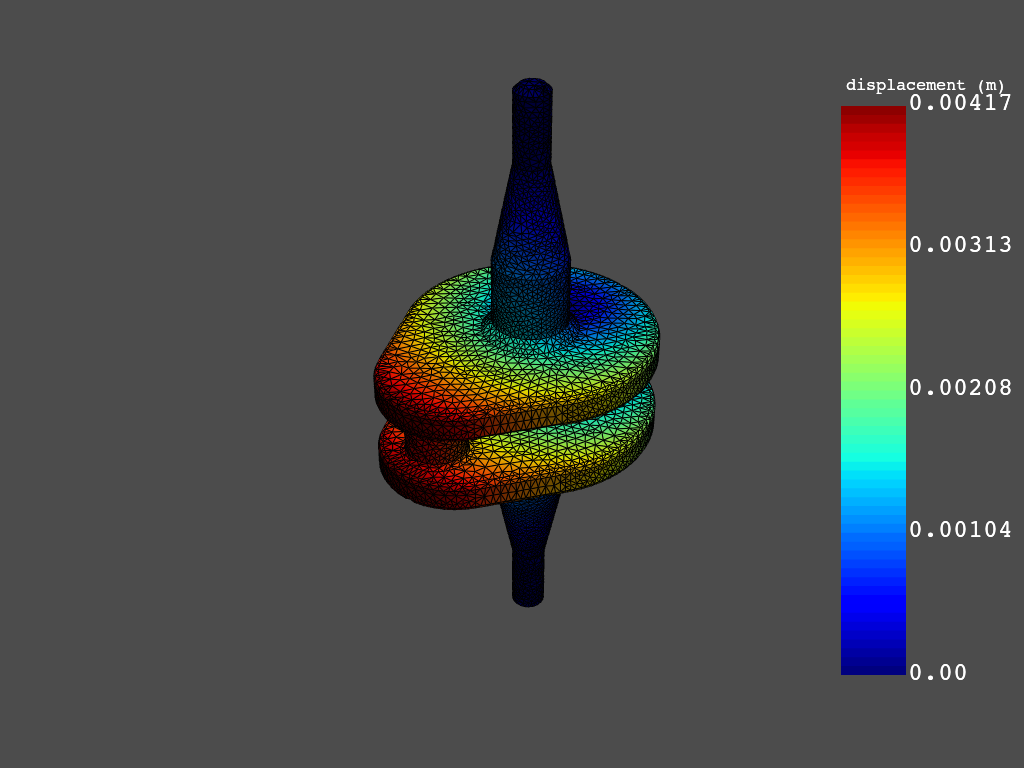
>>> simulation = post.load_simulation(examples.download_crankshaft())
>>> displacement = simulation.displacement()
>>> print(displacement)
results U
set_id 3
node comp
4872 X -3.41e-05
Y 1.54e-03
Z -2.64e-06
9005 X -5.56e-05
Y 1.44e-03
Z 5.31e-06
...
>>> displacement.plot()
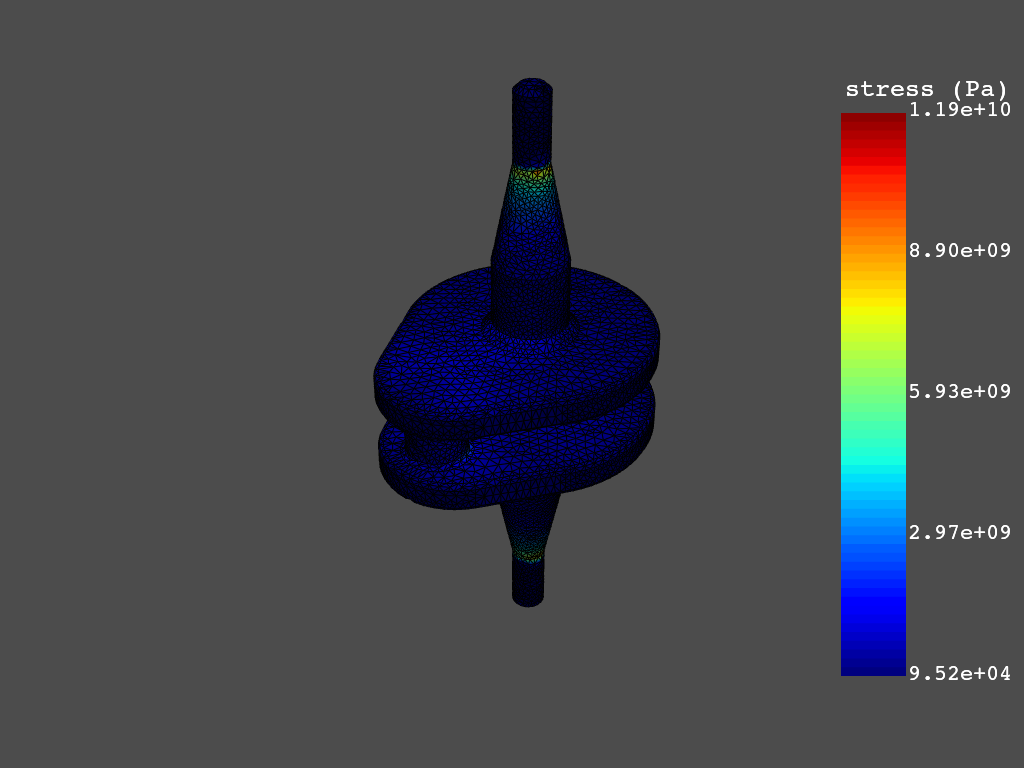
>>> stress_eqv = simulation.stress_eqv_von_mises_nodal()
>>> stress_eqv.plot()
To run PyDPF-Post with Ansys 2021 R1 through 2022 R2, use this code to start the legacy PyDPF-Post tools:
>>> from ansys.dpf import post
>>> from ansys.dpf.post import examples
>>> solution = post.load_solution(examples.download_crankshaft())
>>> stress = solution.stress()
>>> stress.eqv.plot_contour(show_edges=False)

For comprehensive examples of how you use PyDPF-Post, see Examples.
Key features#
Computational efficiency
PyDPF-Post is based on DPF, whose data framework localizes loading and postprocessing on the DPF server, enabling rapid postprocessing workflows because they are written in C and FORTRAN. Because PyDPF-Post presents results in a Pythonic manner, you can rapidly develop simple or complex postprocessing scripts.
Easy to use
The PyDPF-Post API automates the use of chained DPF operators to make postprocessing easier. The PyDPF-Post documentation describes how you can use operators to compute results. This allows you to build your own custom, low-level scripts to enable fast postprocessing of potentially multi-gigabyte models using PyDPF-Core.
Documentation and issues#
Documentation for the latest stable release of PyDPF-Post is hosted at PyDPF-Post documentation.
In the upper right corner of the documentation’s title bar, there is an option for switching from viewing the documentation for the latest stable release to viewing the documentation for the development version or previously released versions.
You can also view or download the PyDPF-Post cheat sheet. This one-page reference provides syntax rules and commands for using PyDPF-Post.
On the PyDPF-Post Issues page, you can create issues to report bugs and request new features. On the PyDPF-Post Discussions page or the Discussions page on the Ansys Developer portal, you can post questions, share ideas, and get community feedback.
To reach the project support team, email pyansys.core@ansys.com.