Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Extract cyclic results#
This example uses a modal analysis with cyclic symmetry to show how to expand the mesh and results.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports. This example uses a supplied file that you can
get by importing the DPF examples package.
from ansys.dpf import post
from ansys.dpf.post import examples
Get Simulation object#
Get the Simulation object that allows access to the result. The Simulation
object must be instantiated with the path for the result file. For example,
"C:/Users/user/my_result.rst" on Windows or "/home/user/my_result.rst"
on Linux.
example_path = examples.find_simple_cyclic()
simulation = post.ModalMechanicalSimulation(example_path)
# print the simulation to get an overview of what's available
print(simulation)
Modal Mechanical Simulation.
Data Sources
------------------------------
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.10.19/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ansys/dpf/core/examples/result_files/file_cyclic.rst
DPF Model
------------------------------
Modal analysis
Unit system: MKS: m, kg, N, s, V, A, degC
Physics Type: Mechanical
Available results:
- node_orientations: Nodal Node Euler Angles
- displacement: Nodal Displacement
- stress: ElementalNodal Stress
- elemental_volume: Elemental Volume
- stiffness_matrix_energy: Elemental Energy-stiffness matrix
- artificial_hourglass_energy: Elemental Hourglass Energy
- kinetic_energy: Elemental Kinetic Energy
- co_energy: Elemental co-energy
- incremental_energy: Elemental incremental energy
- thermal_dissipation_energy: Elemental thermal dissipation energy
- element_orientations: ElementalNodal Element Euler Angles
- structural_temperature: ElementalNodal Structural temperature
------------------------------
DPF Meshed Region:
51 nodes
4 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
------------------------------
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 30
Cumulative Frequency (Hz) LoadStep Substep Harmonic index
1 670386.325235 1 1 0.000000
2 872361.424038 1 2 0.000000
3 1142526.525324 1 3 0.000000
4 1252446.741551 1 4 0.000000
5 1257379.552140 1 5 0.000000
6 1347919.358013 1 6 0.000000
7 679667.393214 2 1 1.000000
8 679667.393214 2 2 -1.000000
9 899321.218481 2 3 -1.000000
10 899321.218481 2 4 1.000000
11 1128387.049511 2 5 1.000000
12 1128387.049511 2 6 -1.000000
13 708505.071361 3 1 -2.000000
14 708505.071361 3 2 2.000000
15 966346.820117 3 3 2.000000
16 966346.820117 3 4 -2.000000
17 1031249.070606 3 5 -2.000000
18 1031249.070606 3 6 2.000000
19 757366.624982 4 1 -3.000000
20 757366.624982 4 2 3.000000
21 926631.623058 4 3 -3.000000
22 926631.623058 4 4 3.000000
23 1035144.649248 4 5 3.000000
24 1035144.649248 4 6 -3.000000
25 807882.379030 5 1 4.000000
26 856868.410638 5 2 4.000000
27 1063247.283632 5 3 4.000000
28 1185511.741334 5 4 4.000000
29 1278969.844256 5 5 4.000000
30 1355579.879820 5 6 4.000000
Extract expanded displacement normal#
displacement_norm = simulation.displacement(
norm=True,
expand_cyclic=True,
)
print(displacement_norm)
displacement_norm.plot()
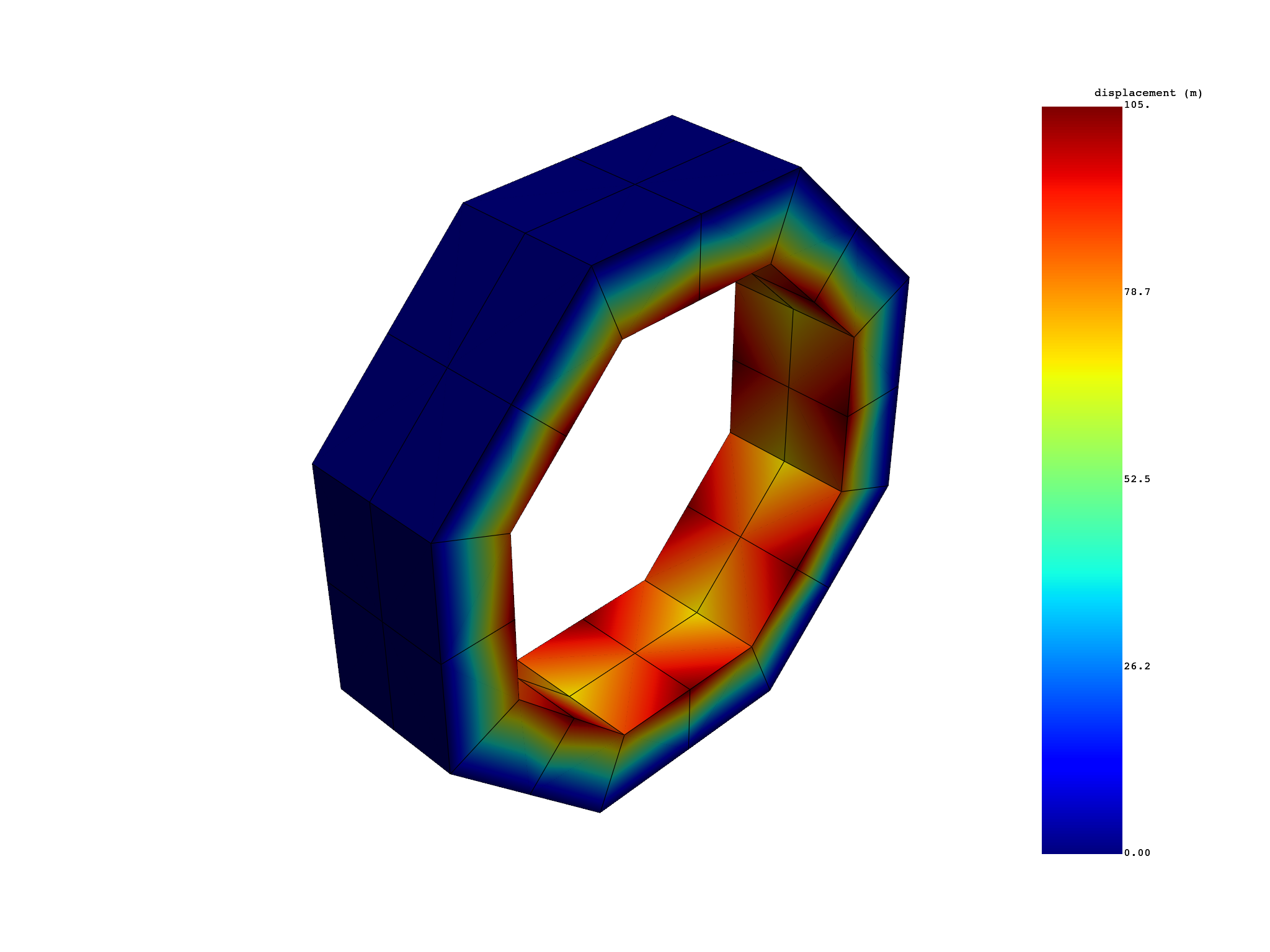
results U_N (m)
set_ids 1
node_ids
1 8.5207e+01
52 8.5207e+01
103 8.5207e+01
154 8.5207e+01
205 8.5207e+01
256 8.5207e+01
... ...
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f77019c9660>)
Extract equivalent von Mises nodal stress expanded on first four sectors#
stress_vm_sectors_1_2_3_4 = simulation.stress_eqv_von_mises_nodal(
expand_cyclic=[1, 2, 3, 4],
)
print(stress_vm_sectors_1_2_3_4)
stress_vm_sectors_1_2_3_4.plot()
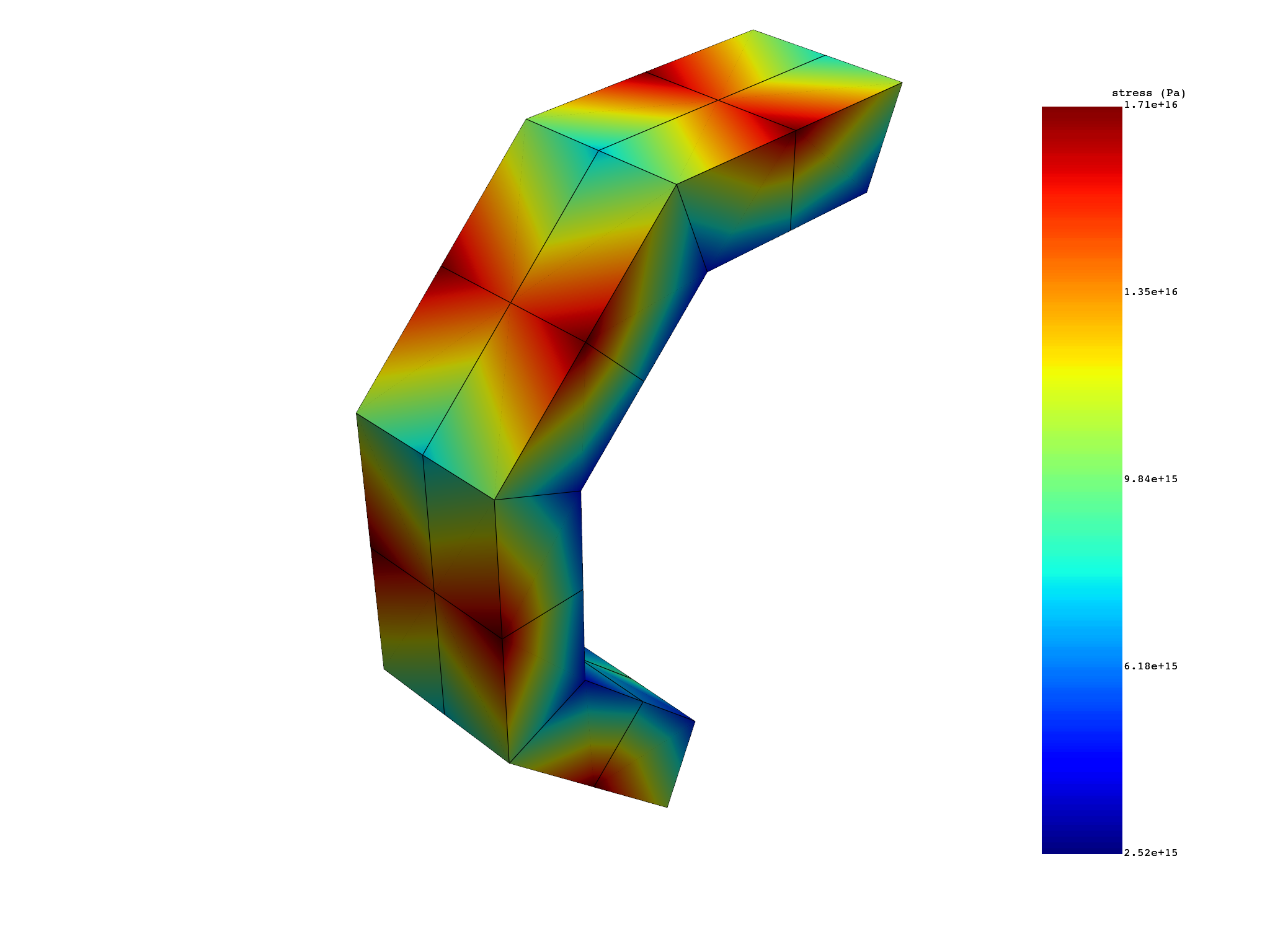
results S_VM (Pa)
set_ids 1
node_ids
1 7.6536e+15
14 9.2247e+15
15 4.6219e+15
18 6.4123e+15
2 1.4681e+16
6 7.9359e+15
... ...
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f77019c8a90>)
Extract equivalent von Mises nodal stress without expansion#
stress_vm_sector_1 = simulation.stress_eqv_von_mises_nodal(
expand_cyclic=False,
)
print(stress_vm_sector_1)
stress_vm_sector_1.plot()
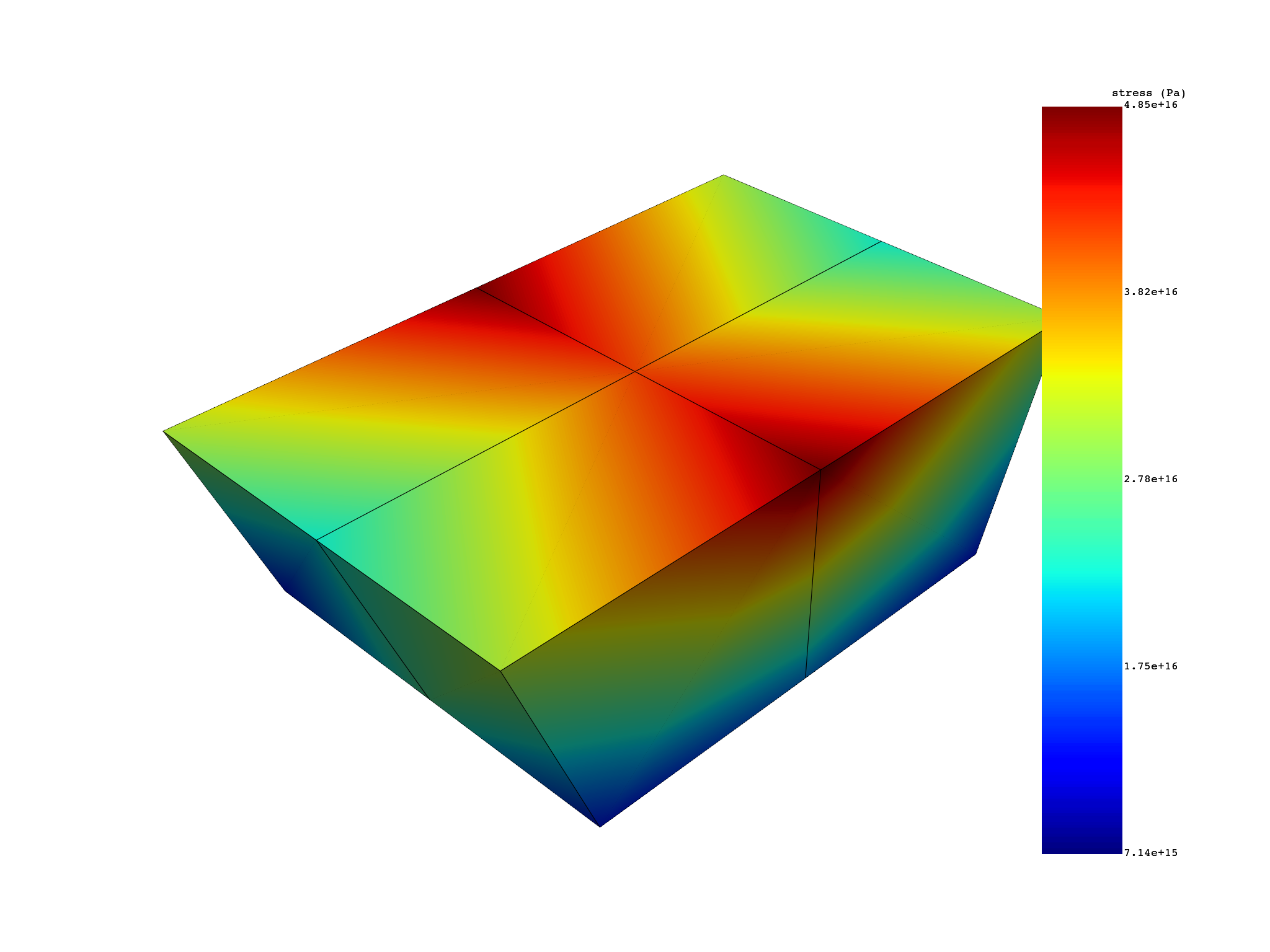
results S_VM (Pa)
set_ids 1
base_sector 1
node_ids
1 2.1648e+16
14 2.6092e+16
15 1.3073e+16
18 1.8137e+16
2 4.1523e+16
6 2.2446e+16
... ...
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f77166122c0>)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.230 seconds)

